When was the last time you turned the key in your vehicle’s ignition, and it just… clicked? We’ve all been there: that moment of panic when you realise your battery is dead. But did you know that one of the main culprits behind battery failure is a process called sulfation?
Well, maintaining the battery of your car and bike is very important. But as much as you care for external damages and the expiry of the battery, you must also keep an eye on problems arising due to internal chemical reactions in the battery. Internal chemical reactions can also reduce the battery’s performance and life. This internal reaction process is known as Sulphation.
Understanding sulfation and how to prevent it can save you from inconvenient breakdowns and extend the life of your battery. So, let’s dive into the world of batteries and explore the ins and outs of sulfation.
What is Sulfation?
Sulfation is the buildup of lead sulfate crystals on the plates of a lead-acid battery. This process occurs during normal battery operation but can become problematic if not addressed.
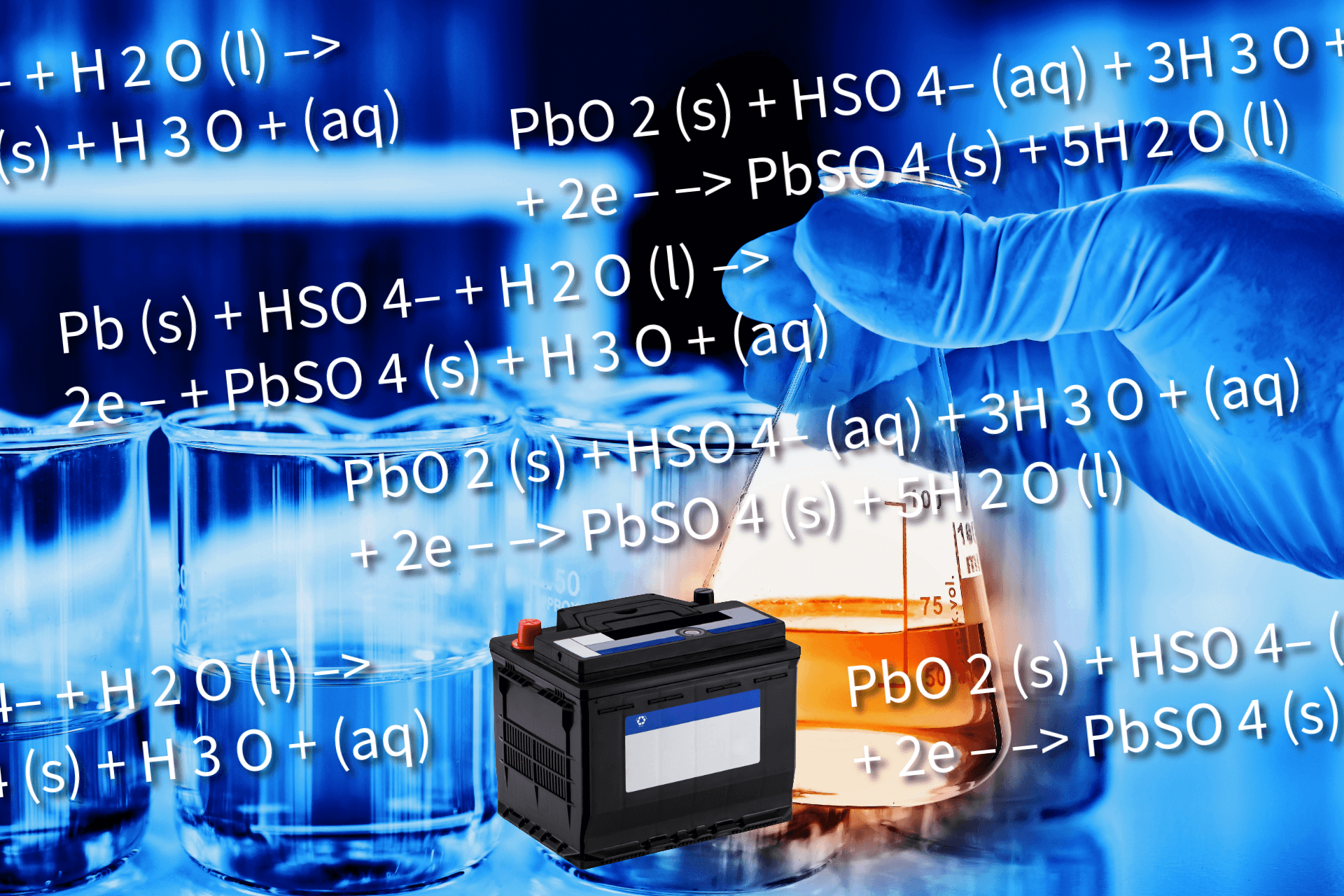
A lead-acid battery is an electrochemical equipment. It converts chemical energy into electrical energy, which powers the electrical system of a car, a bike; or for that matter, when connected to the inverter provides for the power needs of your house or any building.
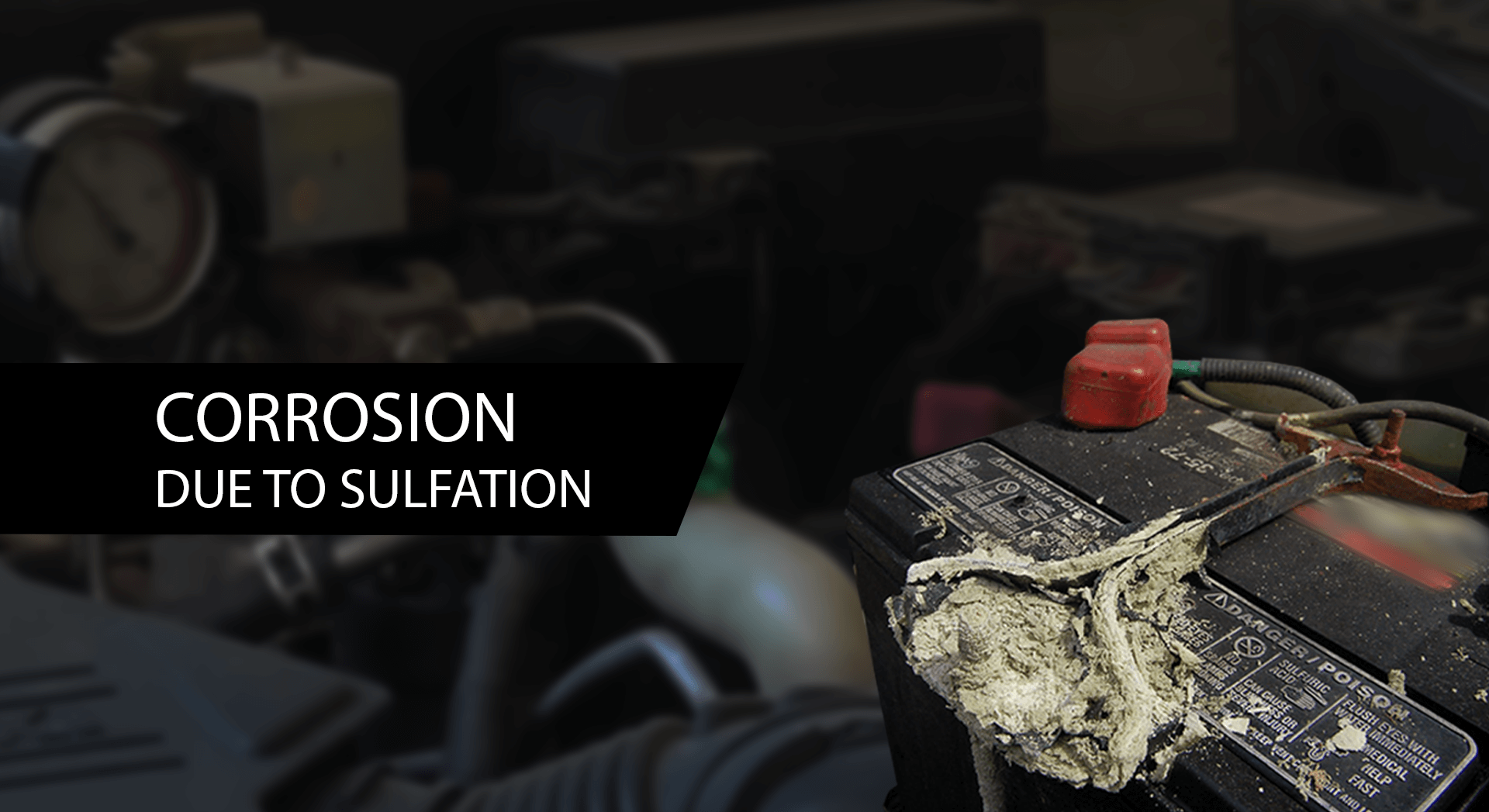
The lead acid battery consists of Sulphuric Acid, and the positive and negative plates are made out of alloy consisting of either lead, antimony or copper. These chemicals react with each other, and the loose electrons from these reactions are used to supply electrical power. In these reactions, as the electrolyte, which is a mixture of Sulphuric Acid, breaks down, Sulphur ions get loose and form crystals. However, when a battery is left idle or not charged properly, sulfur ions can accumulate on the plates, leading to sulfation. This buildup hampers the battery’s performance and can significantly reduce the lifespan of the battery.
What are the Common Causes of Battery Sulfation
Lead acid battery, due to its nature, is bound to experience sulfation. Let us look at common causes that lead to sulfation in a battery. Here are some common reasons why sulfation occurs:
-
Idle Time:
One of the most common causes of sulfation is leaving your battery idle for a long time. It is recommended to start the car battery or a two-wheeler for at least 15 to 20 minutes every week or two. The longer the battery sits idle, the faster it will it sulfate.
-
Low Electrolyte Levels:
When the electrolyte levels go down and remain low for a long time, it exposes the plates. When exposed to air the plates sulfate faster. Monitoring and topping off the electrolyte levels can help avoid this problem.
-
Improper Charging:
To keep your battery in optimal condition, it should be charged to 100% regularly. If a battery is consistently undercharged, it gives room for sulfation since the inactive area of plates starts to sulfate.
Types of Sulfation
Sulfation in lead-acid batteries can be classified into two main types:
-
Reversible Sulfation:
Reversible, as the name suggest is the mild sulfation which can be reversed or treated and get the battery working to its normal potential.
-
Irreversible Sulfation:
As the name suggests, this form of sulfation is more severe and often results in permanent damage to the battery. Irreversible sulfation typically occurs when the battery is when the user does not start the battery for months or the battery is left in a low state of charge for long period of time because of incomplete charging. The lead sulfate crystals become hard and cannot be easily converted back into active materials.
Signs of a Sulfated Battery
So, how can you tell if your battery is starting to sulfate? Here are some common signs to watch for:
-
Difficulty Starting:
If you face a problem starting the vehicle engine, a slow start, or a longer-than-usual start, the battery is possibly going under sulfation. Pay attention to any delays when starting the engine.
-
Reduced Performance:
If your car battery is showing signs of low performance, it is probably sulfating. Signs to watch for are a reduction in the AC’s performance, dimming headlamps, the horn not working or delay in response, and low cabin lights.
-
Visual Inspection:
The visual sign of sulfation can also be seen on the battery terminals. Sulfation leaves a white dust that accumulates on the terminal, causing corrosion of the terminal. If you notice any of these signs, it’s time to act and assess your battery’s condition. Ignoring these signs can lead to more substantial problems down the road.
How to Prevent Sulfation
Taking proper care of your battery and periodic checks is the simplest way to prevent sulfation. Here are a few things you should keep in mind
- Never leave the battery idle for more than a week. Even if you have not taken out your vehicle for months, make sure you start the engine for 15 minutes every week.
- Make sure the battery is not exposed to extreme temperature conditions. Read the user manual for maintaining the battery in your region.
- The more batteries are used, the healthier they are. It all depends on the charge cycles of the battery, meaning the battery must be discharged and charged periodically to maintain chemical reactions.
Conclusion
Sulfation is a common yet often overlooked issue that can significantly impact your battery’s performance and lifespan. By understanding the causes, signs, and preventive measures, you can keep your battery healthy and avoid unexpected failures.
Choose TATA Green Batteries for reliable, long-lasting power, ensuring your vehicle or home is always well-supported. TATA Green Batteries offer consistent performance in different climatic conditions. Choosing TATA Green batteries means investing in top-notch quality and a trusted solution for maintaining optimal battery health.